Filter Blocking Tendencies
Filter Blocking Tendencies
Modern low sulphur Diesels EN590 white Diesel, and BS2869 Red Diesel must conform to a measured level of Filter blocking tendency. The current maximum allowable limit is 2.52 using test method IP387 procedure B. The procedure is passing 300ml of fuel through a 1.6um (micron) disposable filter. As can be seen on the sample below the fuel tested failed FBT and has a reading of above >6.00
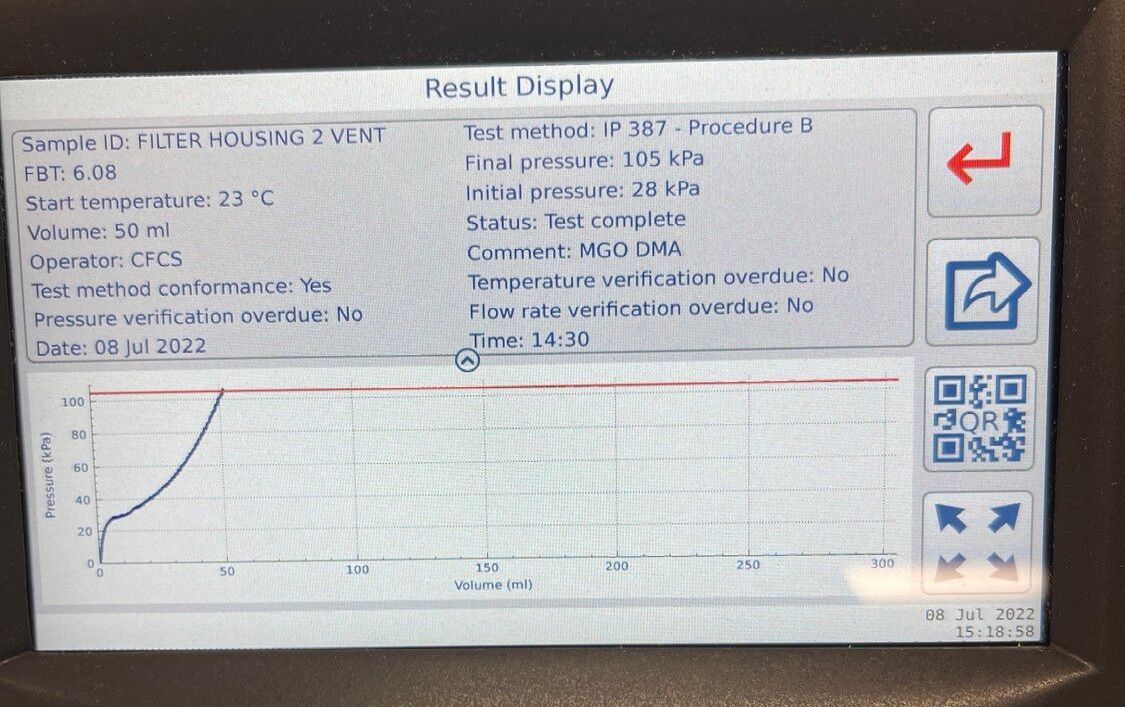
There are several reasons why a fuel can fail FBT testing but the most common effects are the following:
- Cold flow additives de-bonding within the fuel
- Waxing of fuel, due to summer grade been affected by environmental impacts
- Metal Carboxylates (Soaps)
The above can be classed as soluble compounds, just like adding sugar to warm water, the sugar now becomes soluble
Insoluble compounds can be in the form of induced contamination as particulate, just like we experience dust build up in our homes from particulates in the atmosphere.
Soluble and Insoluble compounds and effects
Insoluble compounds within fuel will fall partly under Total contamination within the fuel specifications.
A measurement you may be familiar with is the Particle measurement of liquids referenced to as ISO4406, however ISO4406 is independent of any fuel or oil specification but may be used by OEM manufacturers stating the fuels ISO4406 target level of particulate cleanliness prior to engine filtration.
The world fuel Charter recommend that fuel should be supplied at a ISO4406 particulate level of 18/16/13. Measuring fuel particle contamination considers both the size and number of particles per size class contained in the fuel, i.e. the particle size distribution. The ISO 4406 protocol provides a means of expressing the level of contamination by coding the size distribution. Three code numbers, corresponding to the numbers of particles of size greater than 4, 6 and 14 µm per millilitre.
Particulate Contamination
Fuel injection equipment manufacturers continue to develop fuel injection systems to reduce emissions and fuel consumption and to improve performance. Injection pressures have been increasing; currently, they have reached more than 2000 bars. Such levels of injection pressure demand reduced orifice sizes and component clearances, typically from 2 to 5 µm in injectors. Small, hard particles, which may be carried into these engine parts, are potential sources of engine failure. Excessive diesel fuel contamination can cause premature clogging of diesel fuel filters, depending on the level of both hard and organic particles, and premature wear of modern fuel injection system parts. These impacts, depending on the size and the nature of the particles, will lead to: – Reduced part lifetimes; – Part malfunction; – Engine failure; and – Increased exhaust emissions.
Link to the document https://www.acea.auto/publication/worldwide-fuel-charter-2019-gasoline-and-diesel-fuel/ page 94 onwards for Diesel
Insoluble contamination can be removed from the main fuel tanks by fuel polishing, utilizing different size micron rated media, this would be recommended on a fuel report, works summary after both specification and contamination test suits have been conducted.
Testing just ISO4406, water content and Biological activity is only a snapshot of contamination and does not identify out of specification fuel based on the fuel properties.
The fuel may be out of specification due to soluble compounds suspended within the fuel that will give a high ISO4406 count and the recommendation for fuel polishing would be the wrong course of action, as soluble compounds are not affected by fuel polishing. If we go back to our sugar example once solubilised the sugar is suspended as a liquid within the warm water.
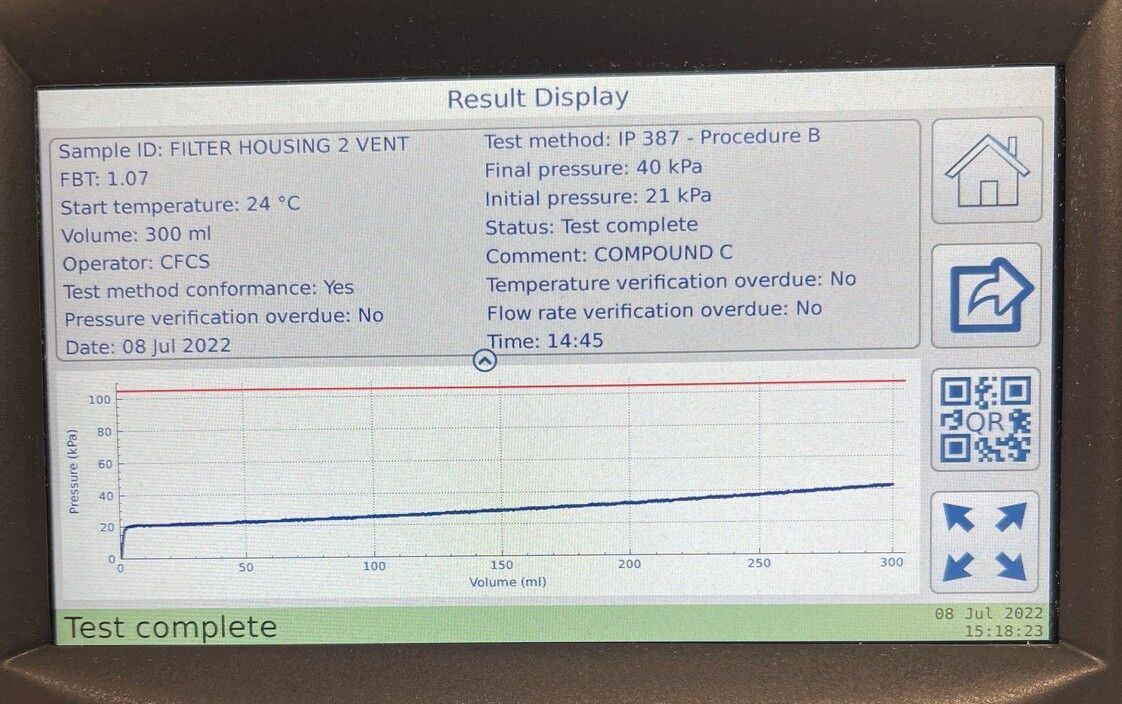
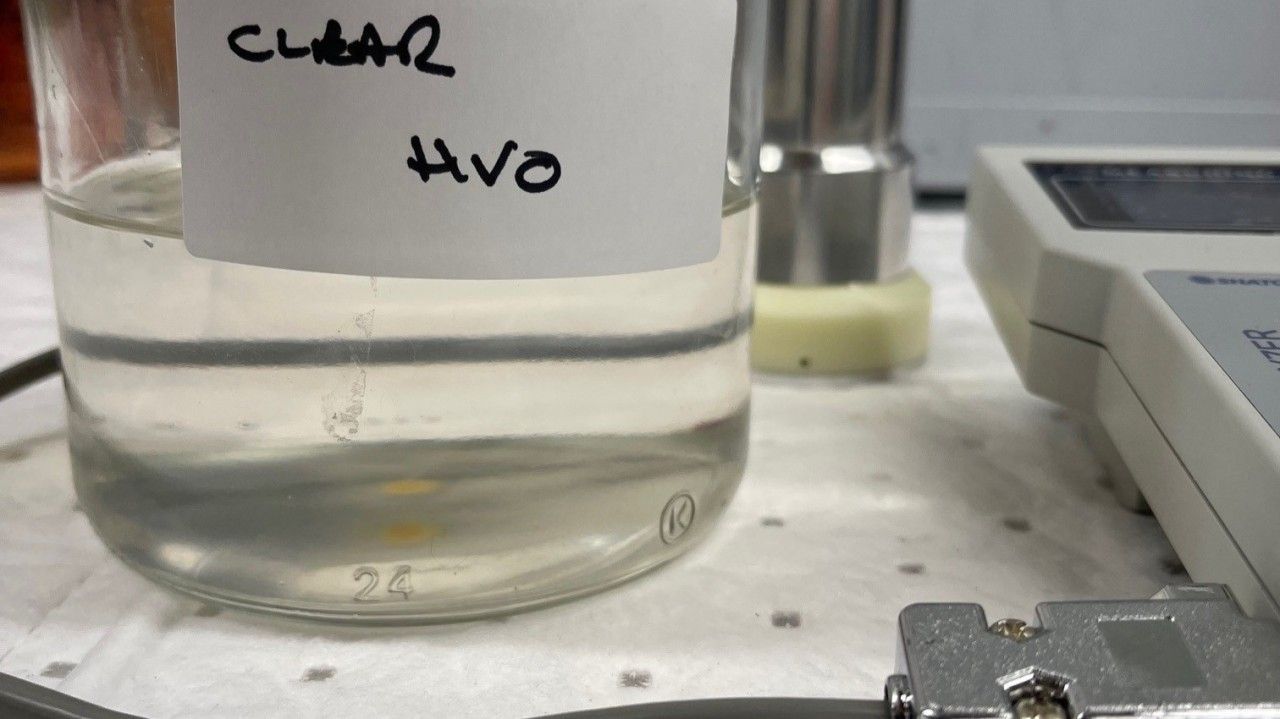
Referencing the first picture of the failed FBT result >6.00 further tests were conducted on this fuel sample to identify the issues. The ISO4406 code was 23/22/20 and hazy, the fuel was additivised with a surfactant based additive and retested. The filter blocking test reduced from >6.00 to 1.07 now within specification, and clear to ASTM D4176 and ISO4406 particulate count of 23/22/20 reduced to 20/18/16. The soluble compounds have now been solubilised within the fuel allowing to identify Insoluble particulate levels, that can now be removed during a fuel polish to the recommended ISO4406 code of 18/16/13 @ 4/6/14 micron.
The Fuel additive used is a product called Aquasolve and has the following effects:
- Water is permanently dissolved in Carbon, Bio and Aviation fuels
- Diesel Bug (bacterial fungus) is cured and then prevented
- Fuel quality is improved reducing consumption by up to 10%
- Reduces harmful emissions by up to 70%
- Reduces Carbon residue in Diesel fuel by 50%
- Cetane Number Increased
- Oxidation stability of Diesel fuel increased by Over 50%
- Prevents rusting and corrosion of components
- Overall engine performance is enhanced, cleansing filters and injectors
- Filter blocking tendency Decreased
- Reduces maintenance costs
- Stabilizes Bio and Ethanol fuels
- Increased Flash Point
- Tested by Intertek to EN590:2013 specifications
- Globally Insured
Coval Technologies completed 12 years of R&D and Independent testing by The City University London.
CFCS Analytical services have also conducted our own case studies and testing on the effects of the product.
Intertek UK have also tested the product and complies with EN590:2013 fuel specification, and therefore does not affect any warranties, or require OEM approval.
For product enquiries please contact cfcs@contaminatedfuel.co.uk





